Fuck LeetCode > Linked List > 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs > Solved in Java, Python, C++, JavaScript, C#, Go, Ruby > Repost or Contribute
LeetCode link: 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs, difficulty: Medium.
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head. You must solve the problem without modifying the values in the list's nodes (i.e., only nodes themselves may be changed.)
Example 1:
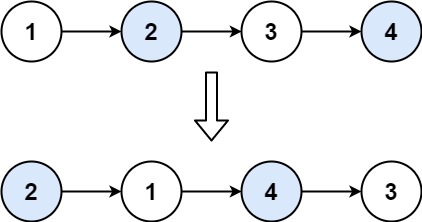
Input: head = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [2,1,4,3]
Example 2:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [1]
Output: [1]
Example 4:
Input: head = [1,2,3]
Output: [2,1,3]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 100
Intuition
Before solving this problem, it is recommended to solve the simple problem 206. Reverse Linked List first.
- To solve this problem, you still need to define at least two variables:
currentandprevious. - The loop condition should be
while (current.next != null)instead ofwhile (current != null), because the operations that need to be performed includecurrent.next.next.
Steps
Traverse all nodes.
var previous = null; var current = head; while (current != null) { current = current.next; }Because every two nodes swap positions, it is necessary to change it to taking two steps at a time.
var previous = null; var current = head; while (current != null && current.next != null) { // 1 var nextNext = current.next.next; // 2 current = nextNext; // 3 }Swap the positions of
currentandcurrent.next.var previous = null; var current = head; while (current != null && current.next != null) { var nextNext = current.next.next; current.next.next = current; // 1 current.next = nextNext; // 2 current = nextNext; }Process
previous.var previous = null; var current = head; while (current != null && current.next != null) { var nextNext = current.next.next; previous.next = current.next; // 1 current.next.next = current; current.next = nextNext; previous = current; // 2 current = nextNext; }Determine the return value. Because the
headnode will be swapped to the second node when the number of nodes exceeds 1, it is best to add adummy_headnode for unified and convenient processing.var dummyHead = new ListNode(); // 1 dummyHead.next = head; // 2 var previous = dummyHead; // 3 var current = head; while (current != null && current.next != null) { var nextNext = current.next.next; previous.next = current.next; current.next.next = current; current.next = nextNext; previous = current; current = nextNext; } return dummyHead.next; // 4
Complexity
Time complexity
O(N)
Space complexity
O(1)
Java #
/**
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
var dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
var previous = dummyHead;
var current = head;
while (current != null && current.next != null) {
var nextNext = current.next.next;
previous.next = current.next;
current.next.next = current;
current.next = nextNext;
previous = current;
current = nextNext;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
Python #
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy_head = ListNode(next=head)
previous = dummy_head
current = head
while current and current.next:
next_next = current.next.next
previous.next = current.next
current.next.next = current
current.next = next_next
previous = current
current = next_next
return dummy_head.next
C++ #
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
auto dummy_head = new ListNode(0, head);
auto previous = dummy_head;
auto current = head;
while (current != nullptr && current->next != nullptr) {
auto next_next = current->next->next;
previous->next = current->next;
current->next->next = current;
current->next = next_next;
previous = current;
current = next_next;
}
auto result = dummy_head->next;
delete dummy_head;
return result;
}
};
JavaScript #
/**
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
var swapPairs = function (head) {
const dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head)
let previous = dummyHead
let current = head
while (current != null && current.next != null) {
const nextNext = current.next.next
previous.next = current.next
current.next.next = current
current.next = nextNext
previous = current
current = nextNext
}
return dummyHead.next
};
C# #
/**
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution
{
public ListNode SwapPairs(ListNode head)
{
var dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
var previous = dummyHead;
var current = head;
while (current != null && current.next != null)
{
var nextNext = current.next.next;
previous.next = current.next;
current.next.next = current;
current.next = nextNext;
previous = current;
current = nextNext;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
Go #
/**
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
dummyHead := &ListNode{0, head}
previous := dummyHead
current := head
for current != nil && current.Next != nil {
nextNext := current.Next.Next
previous.Next = current.Next
current.Next.Next = current
current.Next = nextNext
previous = current
current = nextNext
}
return dummyHead.Next
}
Ruby #
# class ListNode
# attr_accessor :val, :next
#
# def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil)
# @val = val
# @next = _next
# end
# end
def swap_pairs(head)
dummy_head = ListNode.new
dummy_head.next = head
previous = dummy_head
current = head
while current && current.next
next_next = current.next.next
previous.next = current.next
current.next.next = current
current.next = next_next
previous = current
current = next_next
end
dummy_head.next
end